源码阅读 (6)TaskScheduler粗解
layout: post title: “TaskScheduler粗解” description: “” category: “spark” tags: [spark] —
接下来我们粗略的分析一下任务的创建和分发过程。
###TaskScheduler介绍
TaskScheduler的主要任务是提交task集合到集群运算并汇报结果。
主要的任务有:
1. 出现shuffle输出丢失需要报告fetch failed错误
2. 碰到straggle任务需要调度到别的节点上重试
3. 为每个TaskSet维护一个TaskSetManager(追踪本地性及错误信息)
###TaskScheduler创建
在SparkContext 粗解中介绍了在SparkContext初始化时创建TaskScheduler和DAGScheduler。这里具体描述一下其创建过程。
SparkContext创建过程中会调用createTaskScheduler函数来启动TaskScheduler任务调度器:
val (sched, ts) = SparkContext.createTaskScheduler(this, master)
createTaskScheduler函数中,TaskScheduler会根据部署方式而选择不同的SchedulerBackend来处理.
#### Local模式
TaskSchedulerImpl 和 LocalBackend模式
case "local" =>
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES, isLocal = true)
val backend = new LocalBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, 1)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
case LOCAL_N_REGEX(threads) =>
def localCpuCount: Int = Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors()
// local[*] estimates the number of cores on the machine; local[N] uses exactly N threads.
val threadCount = if (threads == "*") localCpuCount else threads.toInt
if (threadCount <= 0) {
throw new SparkException(s"Asked to run locally with $threadCount threads")
}
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES, isLocal = true)
val backend = new LocalBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, threadCount)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
case LOCAL_N_FAILURES_REGEX(threads, maxFailures) =>
def localCpuCount: Int = Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors()
// local[*, M] means the number of cores on the computer with M failures
// local[N, M] means exactly N threads with M failures
val threadCount = if (threads == "*") localCpuCount else threads.toInt
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, maxFailures.toInt, isLocal = true)
val backend = new LocalBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, threadCount)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
Spark集群模式
TaskSchedulerImpl 和 SparkDeploySchedulerBackend 模式
case SPARK_REGEX(sparkUrl) =>
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc)
val masterUrls = sparkUrl.split(",").map("spark://" + _)
val backend = new SparkDeploySchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, masterUrls)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
本地集群模式
TaskSchedulerImpl 和 SparkDeploySchedulerBackend 模式
case LOCAL_CLUSTER_REGEX(numSlaves, coresPerSlave, memoryPerSlave) =>
// Check to make sure memory requested <= memoryPerSlave. Otherwise Spark will just hang.
val memoryPerSlaveInt = memoryPerSlave.toInt
if (sc.executorMemory > memoryPerSlaveInt) {
throw new SparkException(
"Asked to launch cluster with %d MB RAM / worker but requested %d MB/worker".format(
memoryPerSlaveInt, sc.executorMemory))
}
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc)
val localCluster = new LocalSparkCluster(
numSlaves.toInt, coresPerSlave.toInt, memoryPerSlaveInt, sc.conf)
val masterUrls = localCluster.start()
val backend = new SparkDeploySchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, masterUrls)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
backend.shutdownCallback = (backend: SparkDeploySchedulerBackend) => {
localCluster.stop()
}
(backend, scheduler)
Yarn-Cluster模式
YarnClusterScheduler 和 CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 模式
case "yarn-standalone" | "yarn-cluster" =>
if (master == "yarn-standalone") {
logWarning(
"\"yarn-standalone\" is deprecated as of Spark 1.0. Use \"yarn-cluster\" instead.")
}
val scheduler = try {
val clazz = Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.YarnClusterScheduler")
val cons = clazz.getConstructor(classOf[SparkContext])
cons.newInstance(sc).asInstanceOf[TaskSchedulerImpl]
} catch {
// TODO: Enumerate the exact reasons why it can fail
// But irrespective of it, it means we cannot proceed !
case e: Exception => {
throw new SparkException("YARN mode not available ?", e)
}
}
val backend = try {
val clazz =
Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.YarnClusterSchedulerBackend")
val cons = clazz.getConstructor(classOf[TaskSchedulerImpl], classOf[SparkContext])
cons.newInstance(scheduler, sc).asInstanceOf[CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend]
} catch {
case e: Exception => {
throw new SparkException("YARN mode not available ?", e)
}
}
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
Yarn-Client模式
YarnClientClusterScheduler 和 YarnClientSchedulerBackend 模式
case "yarn-client" =>
val scheduler = try {
val clazz = Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.YarnScheduler")
val cons = clazz.getConstructor(classOf[SparkContext])
cons.newInstance(sc).asInstanceOf[TaskSchedulerImpl]
} catch {
case e: Exception => {
throw new SparkException("YARN mode not available ?", e)
}
}
val backend = try {
val clazz =
Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.YarnClientSchedulerBackend")
val cons = clazz.getConstructor(classOf[TaskSchedulerImpl], classOf[SparkContext])
cons.newInstance(scheduler, sc).asInstanceOf[CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend]
} catch {
case e: Exception => {
throw new SparkException("YARN mode not available ?", e)
}
}
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
Mesos模式
TaskSchedulerImpl 和 MesosSchedulerBackend 模式
case mesosUrl @ MESOS_REGEX(_) =>
MesosNativeLibrary.load()
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc)
val coarseGrained = sc.conf.getBoolean("spark.mesos.coarse", false)
val url = mesosUrl.stripPrefix("mesos://") // strip scheme from raw Mesos URLs
val backend = if (coarseGrained) {
new CoarseMesosSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, url, sc.env.securityManager)
} else {
new MesosSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, url)
}
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
TaskScheduler、TaskSchedulerImpl、SchedulerBackend之间的关系
TaskScheduler类负责任务调度资源的分配
SchedulerBackend负责与Master、Worker通信,并收集Worker上分配给该应用的资源的使用情况。
下图描述了TaskScheduler、TaskSchedulerImpl、SchedulerBackend之间的UML关系
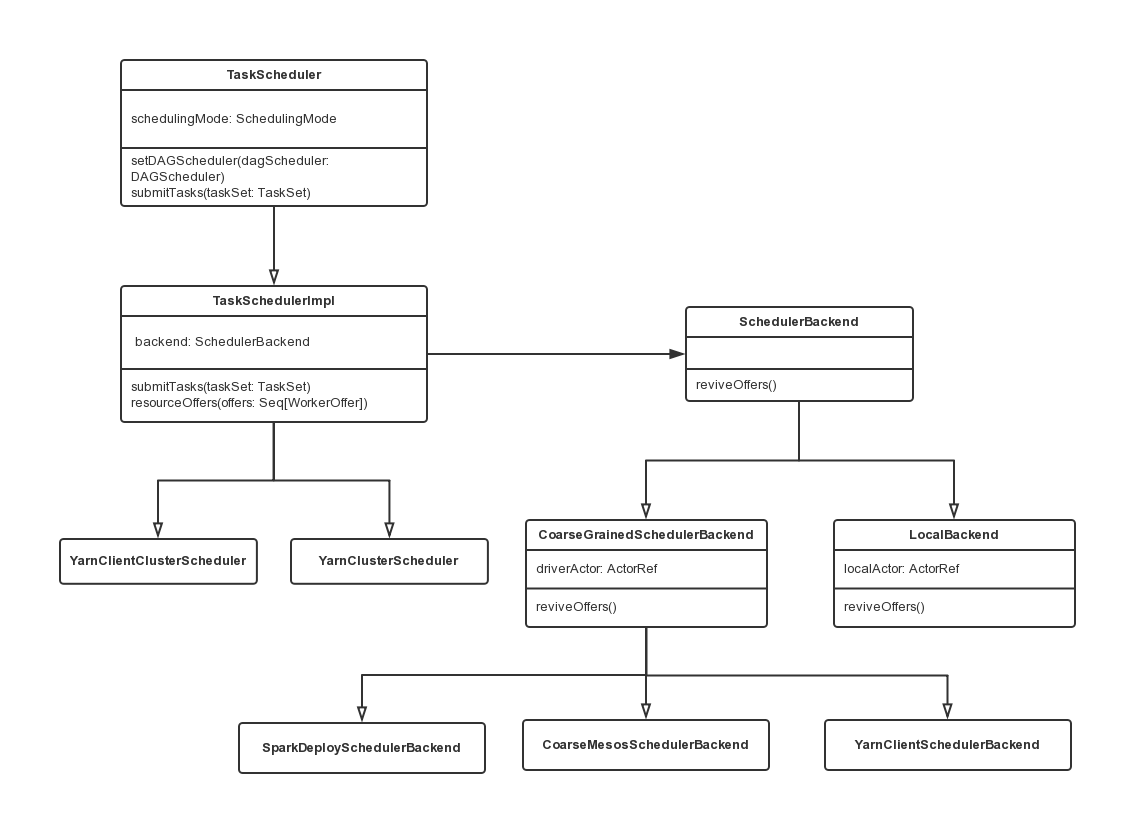
以Spark Standalone集群模式为例
#### 资源信息收集
blog comments powered by Disqus